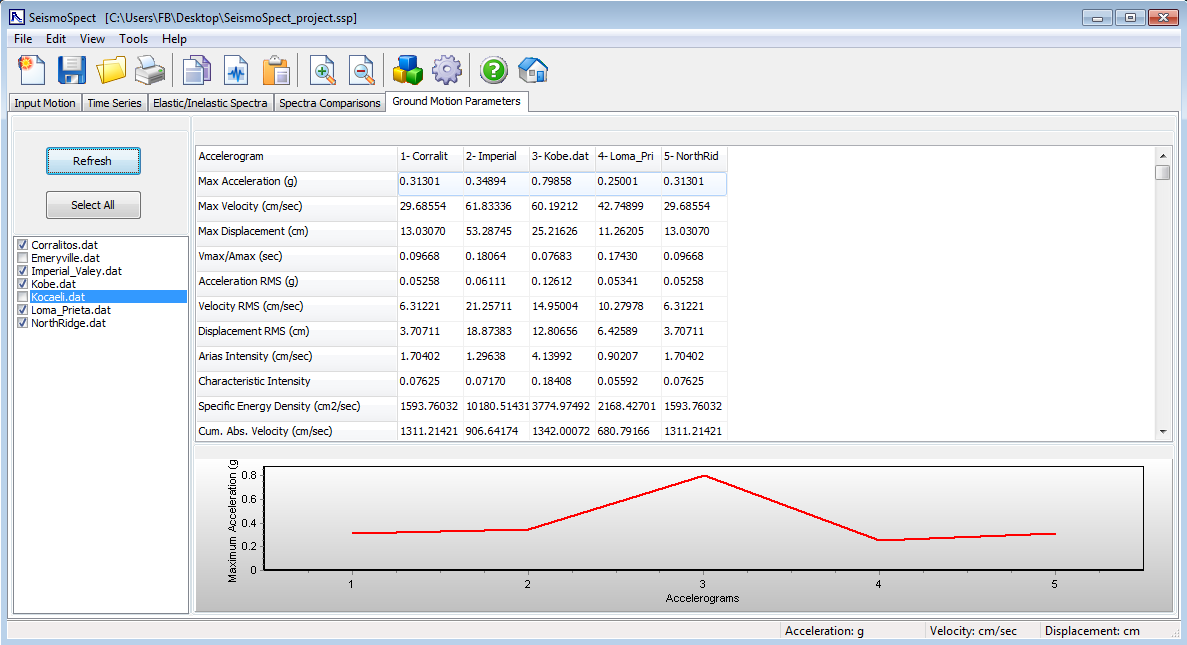
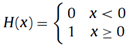Ground Motion Parameters
In this module, a number of commonly computed ground motion parameters are provided, as specified in the Program Settings panel. Users are referred to the work by Kramer [1996] for a detailed description and discussion on the employment of such ground motion quantities. By selecting one of the ground motion parameters from the mentioned table, the results for each matched accelerogram will be show on the chart given at the bottom of the module window.
Peak ground values of acceleration (PGA), velocity (PGV) and displacement (PGD)
![]() ;
; ![]() ;
; ![]()
Peak velocity and acceleration ratio (vmax/amax)
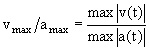
Root-mean-square (RMS) of acceleration, velocity and displacement
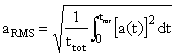 ;
; 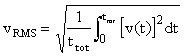 ;
; 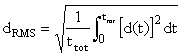
Arias Intensity (Ia)
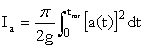
Characteristic Intensity (Ic)
![]()
Specific Energy Density (SED)
![]()
Cumulative Absolute Velocity (CAV)
![]()
Acceleration (ASI) and Velocity (VSI) Spectrum Intensity [Von Thun et al., 1988]
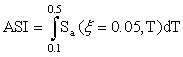 ;
; 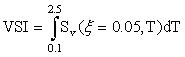
Housner Intensity (HI)
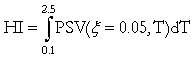
Sustained maximum acceleration (SMA) and velocity (SMV)
Introduced by Nuttli [1979], this parameter gives the sustained maximum acceleration/velocity during three cycles, and is defined as the third highest absolute value of acceleration/velocity in the time-history (note: in order for an absolute value to be considered as a "maximum", it must be larger than values 20 steps before and 20 steps after).
Effective Design Acceleration (EDA)
This parameter corresponds to the peak acceleration value found after lowpass filtering the input time history with a cut-off frequency of 9 Hz [Benjamin and Associates, 1988].
A95 parameter [Sarma and Yang, 1987]
The acceleration level below which 95% of the total Arias intensity is contained. In other words, if the entire accelerogram yields a value of Ia equal to 100, the A95 parameter is the threshold of acceleration such that integrating all the values of the accelerogram below it, one gets an Ia=95.
Predominant Period (Tp)
The predominant period (Tp) is the period at which the maximum spectral acceleration occurs in an acceleration response spectrum calculated at 5% damping.
Significant duration
The interval of time over which a proportion (percentage) of the total Arias Intensity is accumulated (default is the interval between the 5% and 95% thresholds).
Maximum Incremental Velocity [MIV]
The Maximum Incremental Velocity (MIV) is defined as the maximum area under the acceleration curve between two zero crossings of the accelerogram. Users are referred to the works by Anderson and Bertero [1987] and Guaman [2010] for further information for description and discussion on the topic.
Damage Index
The Damage Index is calculated as the summation of the amplitudes of the cycles in the accelerogram raised to the c exponent, determining the relative importance of different amplitude cycles, and multiplied by the C linear scale factor as proposed by Malhotra [2002]. The cycles and the corresponding cycle amplitudes for the accelerogram are identified through a rainflow counting algorithm as described by ASTM [1985], the values of the exponent c and the multiplier C can be defined in the Ground Motion Parameters Menu. The procedure is summarized by Hancock and Bommer [2005].
Number of Effective Cycles
The Number of Effective cycles is calculated as the summation of the ratios of the amplitudes of the cycles in the accelerogram divided by the maximum cycle amplitude and raised to the c exponent, determining the relative importance of different amplitude cycles, as proposed by Malhotra [2002]. The cycles and the corresponding cycle amplitudes for the accelerogram are identified through a rainflow counting algorithm as described by ASTM [1985] and the value of the c exponent can be defined in the Ground Motion Parameters Menu. The procedure is summarized by Hancock and Bommer [2005].
Impulsivity Index (IP) [Panella et al., 2017]
The Impulsivity index is an indicator of the impulsive character of the ground motion and is calculated as the developed length of velocity of the velocity time-series divided by the Peak Ground Velocity.
Average Spectral Acceleration (Sa,avg/AvgSa) [Bianchini et al. 2009]
The Average Spectral Acceleration is computed as the geometric mean of the spectral pseudo-acceleration ordinates for a 5% damping according to Bianchini et al. [2009]. The maximum and minimum periods and the period step of the spectrum used for the computation of the Average Spectral acceleration can be defined in the Ground Motion Parameters Menu.
Standardized Cumulative Absolute Velocity (CAVSTD) [Campbell and Bozorgnia 2011]
The Standardized Cumulative Absolute Velocity is defined from equation:
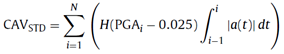
where N is the number of discrete 1-s time intervals, PGAi is the value of the peak ground acceleration (g) in time interval i (inclusive of the first and last values), and H(x) is the Heaviside Step Function, defined by the expression: